Input validation
Every piece of information which server received from arbitrary client can be either valid or invalid. There are generally two main reasons of invalid input:
- The client is out of sync – e.g.: tries to register same account twice.
- The client tries to perform some malicious action.
Both cases can lead to inconsistency, unauthorised behaviour or data leaks and you usually cannot tell for sure whether your application is under attack or whether it is just a random error. You have to check the format of incoming data and also whether the user which is trying to perform an action has privilege to access given information or perform given action at all – e.g.: user can modify his own profile but should not be able to modify others’ profiles.
Here is a short list of what actions should be taken care of when parsing input:
- Required inputs should have values – at least use
isset()orempty(). - Always check format of incoming data:
- Numbers should be floats or integers – use
floatval()orintval()to parse them. - Date, email, phone, URL, … should have given format – there are libraries for form input validations, try to use them – implementation of such logic is quiet complex.
- Use custom validation rules for specific data: SSN, tax ID, credit card number… Some of them can be checked by regular expression, some of them require calculations.
- Numbers should be floats or integers – use
- Use functions like PDO’s
bindValue()to safely pass values into database and avoid SQL injection. - Do not use cookies to store visitor’s identity. Store user ID into server session.
- Check whether currently authorised user is allowed to perform requested action.
- Always check relationship between currently authorised user and records which he tries to create, read or modify.
- Use database constraints (foreign and unique keys) to prevent redundancy.
The session can be hijacked (take session ID from cookies and try to apply it in another browser). There is not much you can do about it except using HTTPs to prevent attackers from reading network traffic contents.
Importance of server-side validation
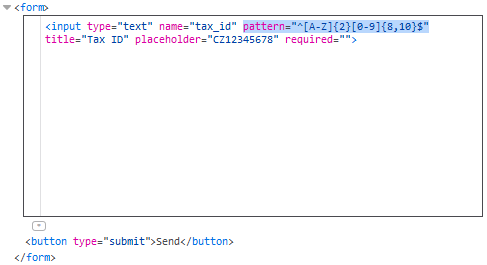
Even though your application generates nice user interface with form fields using correct type, equipped with
required attribute and even pattern for regular expression check, the visitor can use developer tools to
modify currently displayed HTML or create his own form/script which submits data against your server backend.
<form>
<input type="text" name="tax_id" pattern="^[A-Z]{2}[0-9]{8,10}$" title="Tax ID" placeholder="CZ12345678" required>
<button type="submit">
Send
</button>
</form>
Following image shows capability of developer tools (removing the pattern attribute):
The result of this is that you cannot rely on client-side validations which you set for inputs. It is a mere front end visual effect.
The client-side validations are still a good thing for 99.9% of users because they can be quickly informed about an error without submitting the form.
The same rules also applies for data stored in cookies as they can also be accessed and modified with developer tools (in storage tab).
Summary
Always validate incoming data on backend and check user identity and authorize each action. Take a look at other articles about security risks too, because it is also your responsibility as a developer to protect other users from being attacked through your application. It is also a good idea to use logger which can store every action performed and details about it to reconstruct possible reasons of error or data leak.
