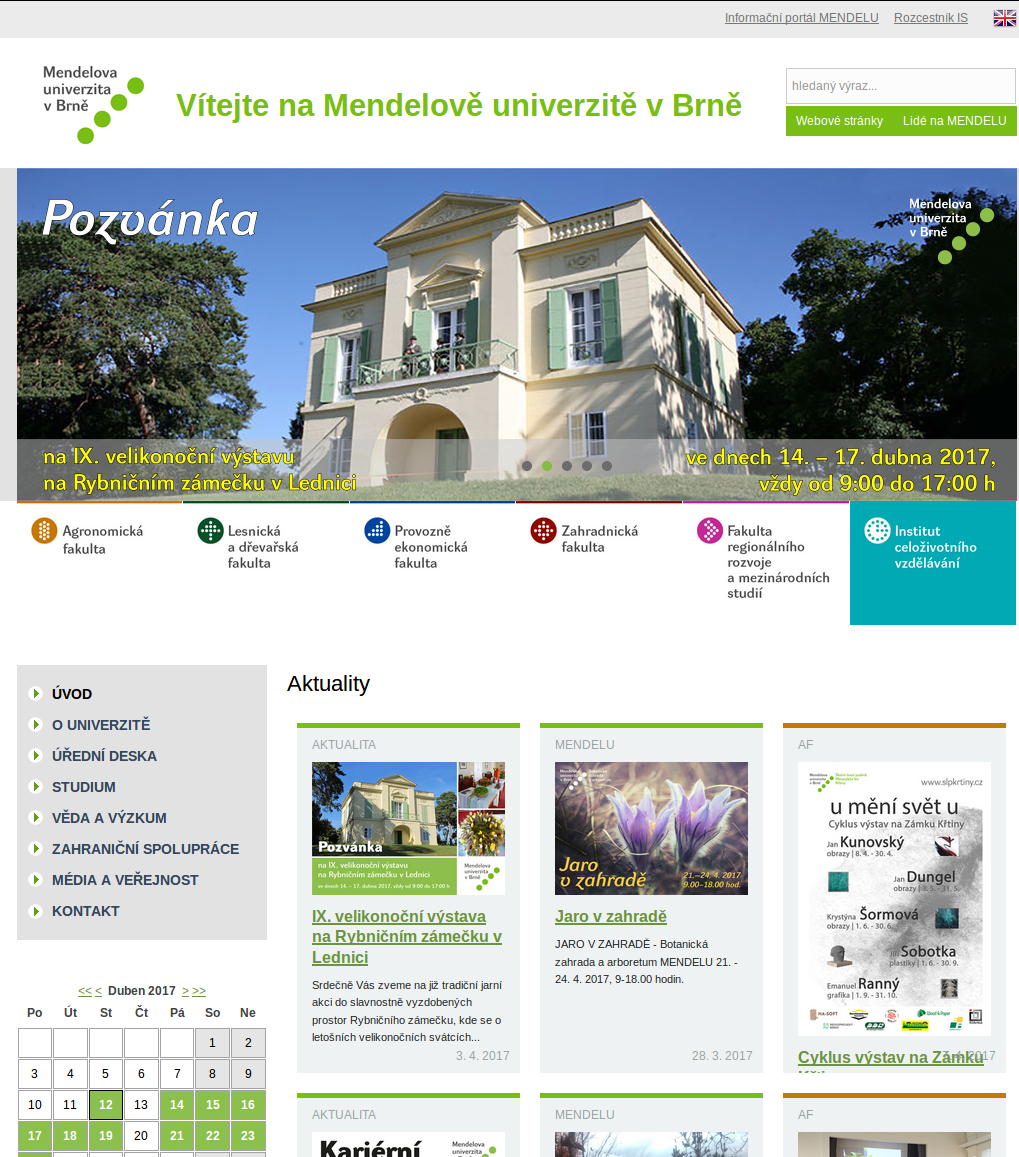
Web Applications - technical aspects
- Single page is composed from many small components
- Main HTML file
- CSS files
- Files with JavaScript code
- Multimedia (images, video…)
- Embedded components (i.g. maps, like/share buttons)
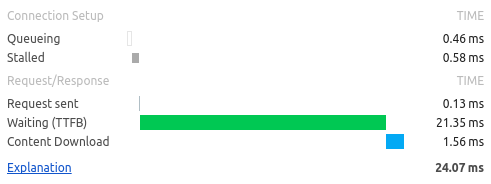
- Sometimes stored on multiple servers – load speed is crucial to keep visitor interested
- Maximal amount of connections per host
- Speed of connection and latency
Visitors’ point of view
HTTP point of view
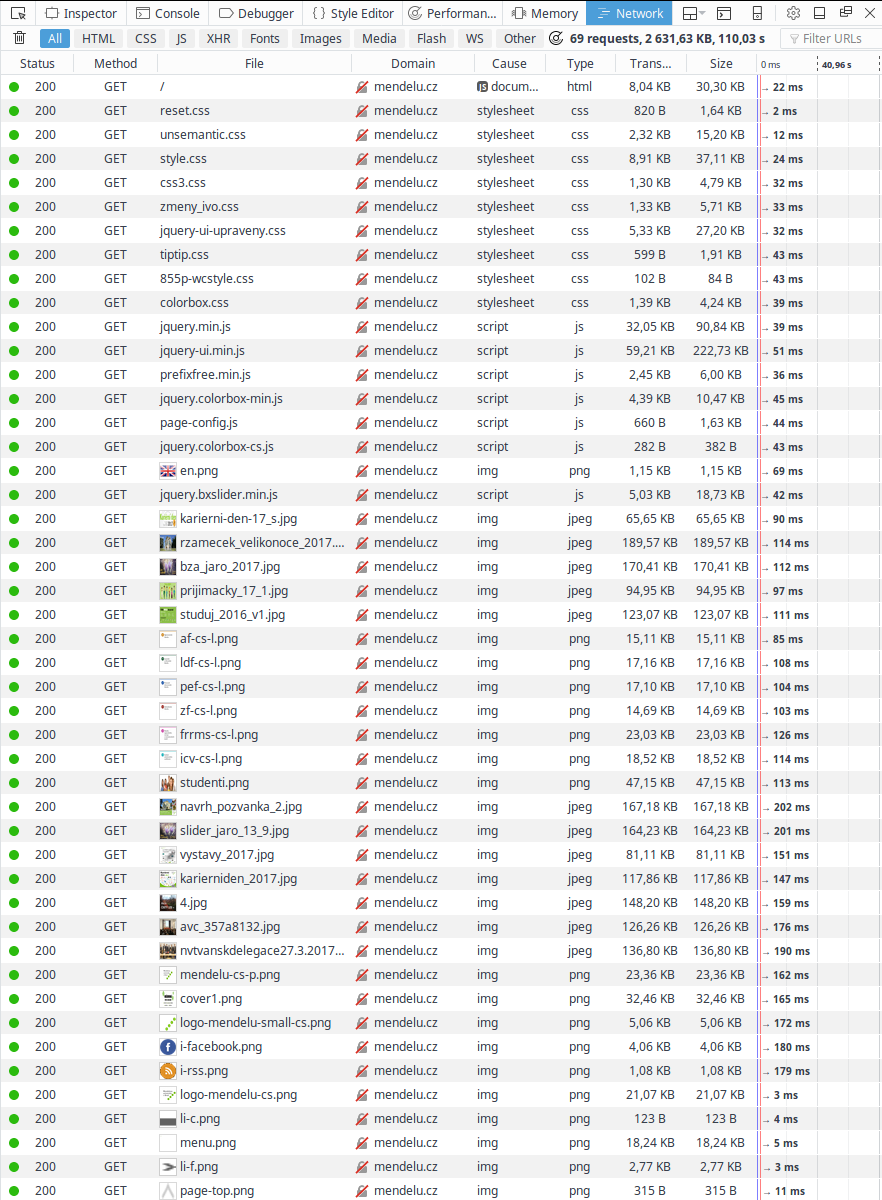
Anatomy of HTTP request
Web Applications - sandboxed network application
- There are things that you cannot influence
- Speed and quality of connection
- Execution environment (browser)
| Download from mendelu.cz | Download from nasa.org |
 |
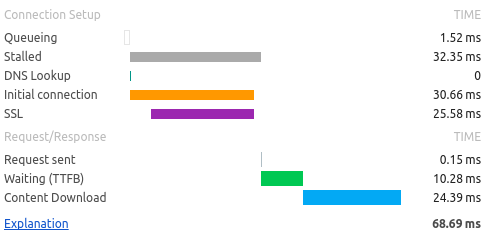 |
Metadata
- Content related
- Charset
- Cache control
- Zoom behaviour for mobile devices
- Search engine crawlers
- Keywords
- Description
- Author
- Only a small impact for SEO
- Not that important for web applications
Cache
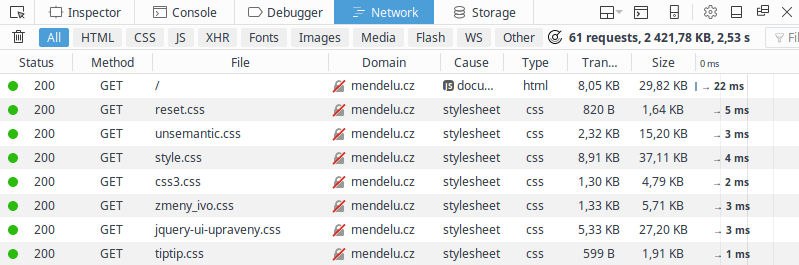
- First visit to a website – browser downloads everything
- Many files are static (files that never change)
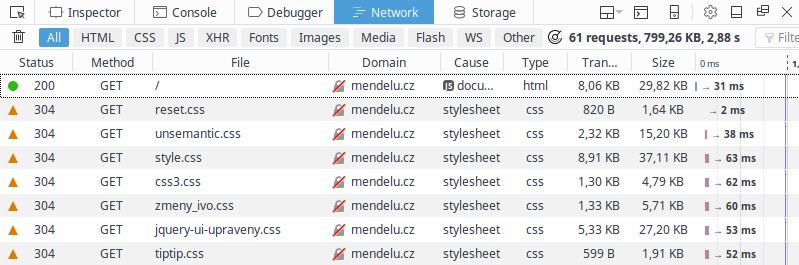
- Next visit – download only modified files
- Cache types
- Local – in your computer (RAM or HDD)
- Shared – for whole organisation/town
- Good for performance
- Problems with dynamic content (login/logout, commercials…)
HTTP Cache management
- Uses HTTP headers
- Set maximal time to store cached content on client
- for defined period of time
- Type of content – private X public
- Client must check for changes
- By last date of content change
- By content hash
| First-time transfer | Subsequent transfers |
 |
 |
Cache control
By last modification
Server:
Last-Modified: Wed, 13 Oct 2004 09:43:02 GMT
Client:
If-Modified-Since: Wed, 13 Oct 2004 09:43:02 GMT
By content
Server:
ETag: "3fe48-527f-52237c0"
Client:
If-None-Match: "3fe48-527f-52237c0"
Web Applications - state management
- Authentication, forms, shopping cart…
- HTTP is stateless
- Server cannot logically connect individual requests
- One page-view is made of many HTTP requests
- Multiple clients request data from server in the same time
- Tracking state is problematic
- IP address
- GET/POST parameters
- Cookies
- Session
Web Applications - state management
- IP address
- one IP may be shared by many machines/users
- IP 6 still not widely available
State - GET/POST parameter
- GET/POST parameters
- dangerous for users
- tedious for programmers
<a href="...&userIdentity=abc123">...</a> <form action="..." method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="userIdentity" value="abc123" />
...
<input type="submit" value="..." />
</form>State - Cookies
- State is stored in browser
- Unreliable - user or software may delete/modify
- Insecure - not encrypted, anybody can access cookies
- Cookies have limited lifespan
- until browser is closed (only in RAM)
- given duration (stored on disk)
- Cookies are automatically attached to every request
- Cookies are attached to a domain that requested to store data in them
- Cookies can store only texts (max 4KiB), transferred along each HTTP request
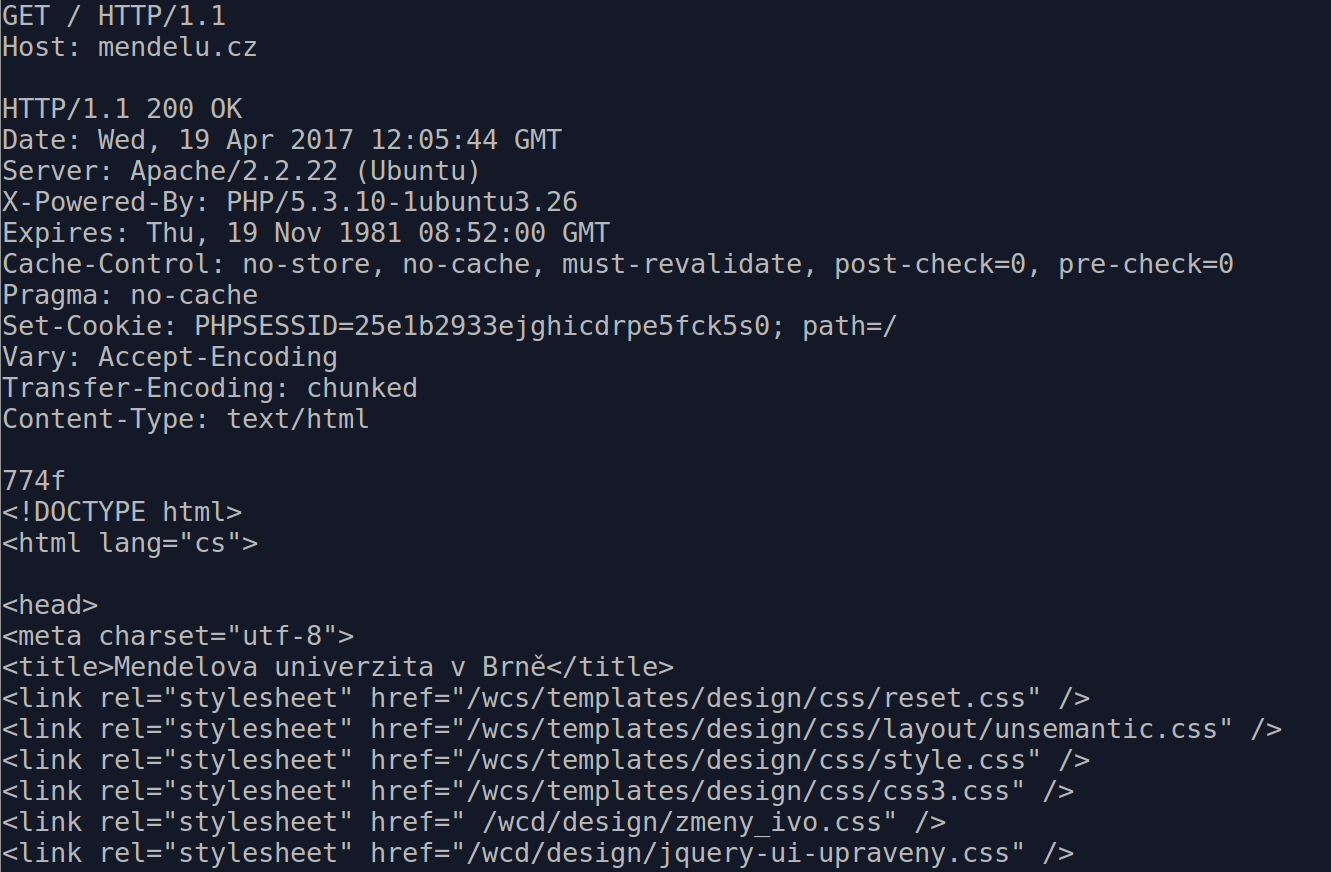
State - Cookies
First client request
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: mendelu.cz
... + empty line
Response from server
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Set-Cookie: name=value
... + empty line
<!DOCTYPE html>
...
Subsequent client requests
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: mendelu.cz
Cookie: name=value
... + empty line
State - Session
- State is stored on server
- Large amount of data can be stored
- Automatic sessions:
- An identification code is generated with first request and send in response to a client
- Data is stored under that identifier on server
- Client stores this identifier into cookie and sends it with subsequent requests
- Server needs to match client with stored content
- Only session identifier is transferred
- Session identifier is weak spot - session hijacking
Session 1
Session 2
Session 3
Session - more clients
Checkpoint
- Does state management based on session require to use cookies?
- Can a HTML form be submitted using GET method?
- Can you store session data in a database?
- How many HTTP requests can be processed between a client and a server at once?
- Can you send an HTTP POST request without HTML form?